VR Simulations in Medical School: Enhancing Clinical Skills and Diagnostic Abilities through Virtual Reality.
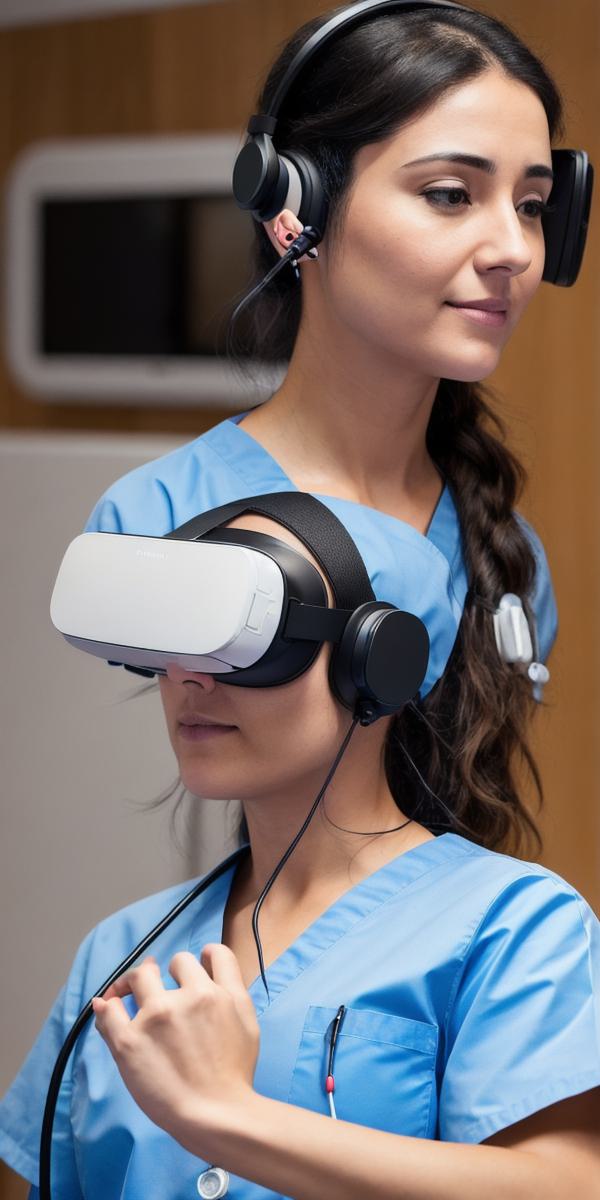

Virtual Reality (VR) simulations are becoming increasingly popular in medical school as a way to enhance clinical skills and diagnostic abilities. With the help of VR, students can practice surgeries, diagnose diseases, and improve their overall performance without putting themselves or others at risk. In this article, we will explore some of the benefits of using VR simulations in medical school and provide examples of how they are being used in real-life settings.
One of the main benefits of VR simulations in medical school is that they allow students to practice surgical procedures without the need for a cadaver or animal subject. This eliminates the risk associated with performing surgeries on real patients, as well as the ethical concerns that arise from using living subjects. For example, at Stanford University School of Medicine, students use VR simulations to perform laparoscopic surgery on a virtual patient, giving them the opportunity to practice their skills in a safe and controlled environment.
In addition to surgical procedures, VR simulations can also be used to diagnose diseases and conditions. By simulating different medical scenarios, students can improve their diagnostic abilities and learn how to make accurate diagnoses in real-life situations. For example, at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF), medical students use a VR simulation called "MedVR" to diagnose virtual patients with various medical conditions such as heart attacks and strokes.
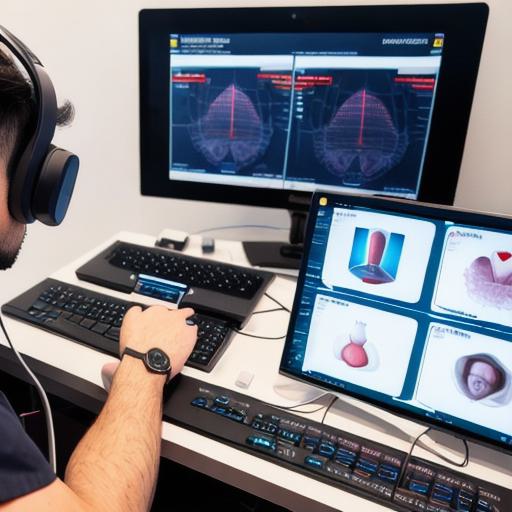
Another benefit of VR simulations is that they can provide personalized learning experiences for each student. With VR, students can work at their own pace and focus on areas where they need the most improvement. This allows for more effective and efficient learning outcomes. For example, at Duke University School of Medicine, medical students use a VR simulation called "MedVR Surgery" to practice surgical procedures in real-time, with feedback from experts tailored specifically to their individual needs.

Research has also shown that using VR simulations in medical school can improve student performance and reduce the risk of medical errors. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that students who used VR simulations for surgical training were more likely to make accurate diagnoses and perform procedures correctly than those who did not use VR.
Overall, VR simulations are an effective way to enhance clinical skills and diagnostic abilities in medical school. By providing a safe and controlled environment for practice, personalized learning experiences, and expert feedback, students can improve their performance and reduce the risk of medical errors. With ongoing advancements in technology, it is likely that VR simulations will continue to play an increasingly important role in medical education in the future.








