AR Applications in Medical Education: Augmenting Learning with Interactive and Visual Experiences
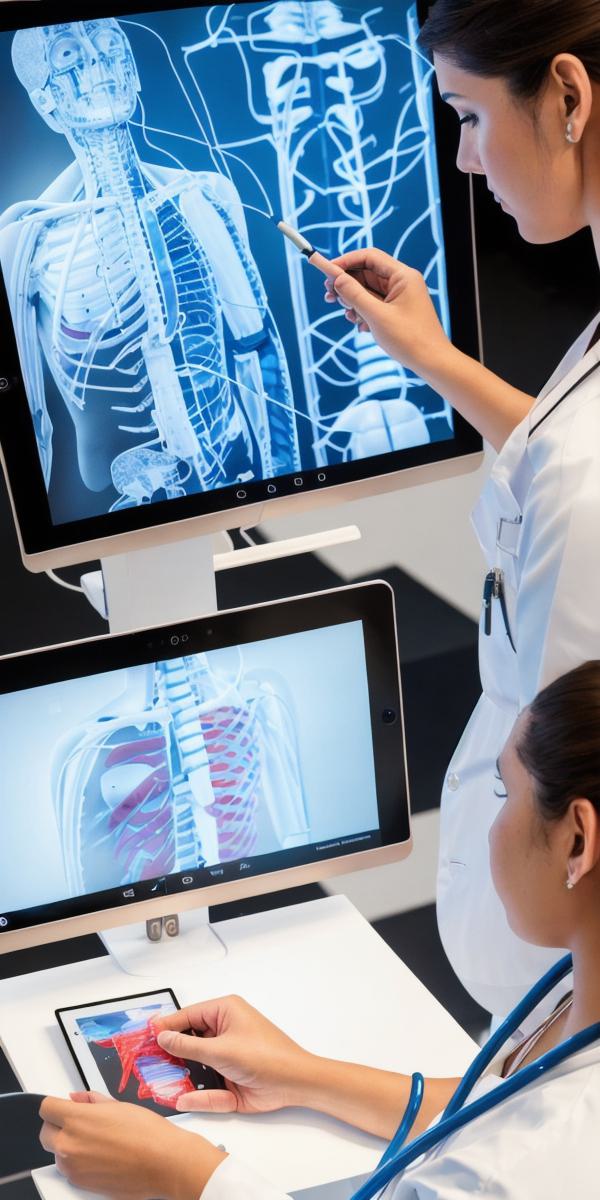
Medical education is a critical component of the healthcare industry, and it plays a vital role in training doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to provide high-quality patient care. However, traditional medical education methods, such as lectures and textbooks, can be limited in their ability to engage and retain students. This is where AR (Augmented Reality) applications come in, augmenting learning with interactive and visual experiences that enhance the learning process and improve student outcomes.
AR technology has been rapidly advancing in recent years, and it has already found its way into various industries, including education. In medical education, AR applications have been used to create immersive and interactive learning experiences that allow students to visualize complex concepts and procedures. For example, AR-powered surgical simulations allow medical students to practice surgical techniques in a safe and controlled environment, while AR-enhanced anatomy lessons enable students to explore the human body in 3D.
One of the key advantages of AR applications in medical education is their ability to provide students with real-time feedback and guidance. By using sensors and other tracking technologies, AR systems can monitor a student’s performance and provide instant feedback on areas where they need improvement. This allows students to learn from their mistakes and adjust their approach in real-time, leading to faster and more effective learning outcomes.
AR applications also have the potential to enhance student engagement and motivation. By providing interactive and visually engaging experiences, AR systems can help students stay focused and interested in the material they are learning. This, in turn, can lead to better retention and a deeper understanding of the concepts being taught.
According to Dr. David Jensen, a professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, “AR applications have the potential to revolutionize medical education by providing students with more engaging and interactive learning experiences. By allowing students to visualize complex concepts and procedures in real-time, AR systems can help them learn more effectively and efficiently.”
Real-life examples of AR applications in medical education include the use of AR-powered surgical simulators at Harvard Medical School, where students can practice surgical techniques on a virtual patient. Another example is the use of AR-enhanced anatomy lessons at the University of California, Irvine, where students can explore the human body in 3D and gain a deeper understanding of its structure and function.
In conclusion, AR applications have the potential to revolutionize medical education by providing students with interactive and visually engaging learning experiences that enhance the learning process and improve student outcomes. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that we will see more and more innovative uses of AR in medical education, leading to a more effective and efficient way of training healthcare professionals.








