VR-based Rehabilitation for Stroke Patients: Accelerating Recovery and Restoring Motor Functions

As technology continues to advance, new and innovative ways to improve healthcare are emerging. One such innovation is the use of virtual reality (VR) in stroke rehabilitation. Stroke is a leading cause of long-term disability, and traditional rehabilitation methods can be time-consuming and costly. However, VR-based rehabilitation has shown promising results in accelerating recovery and restoring motor functions in stroke patients.
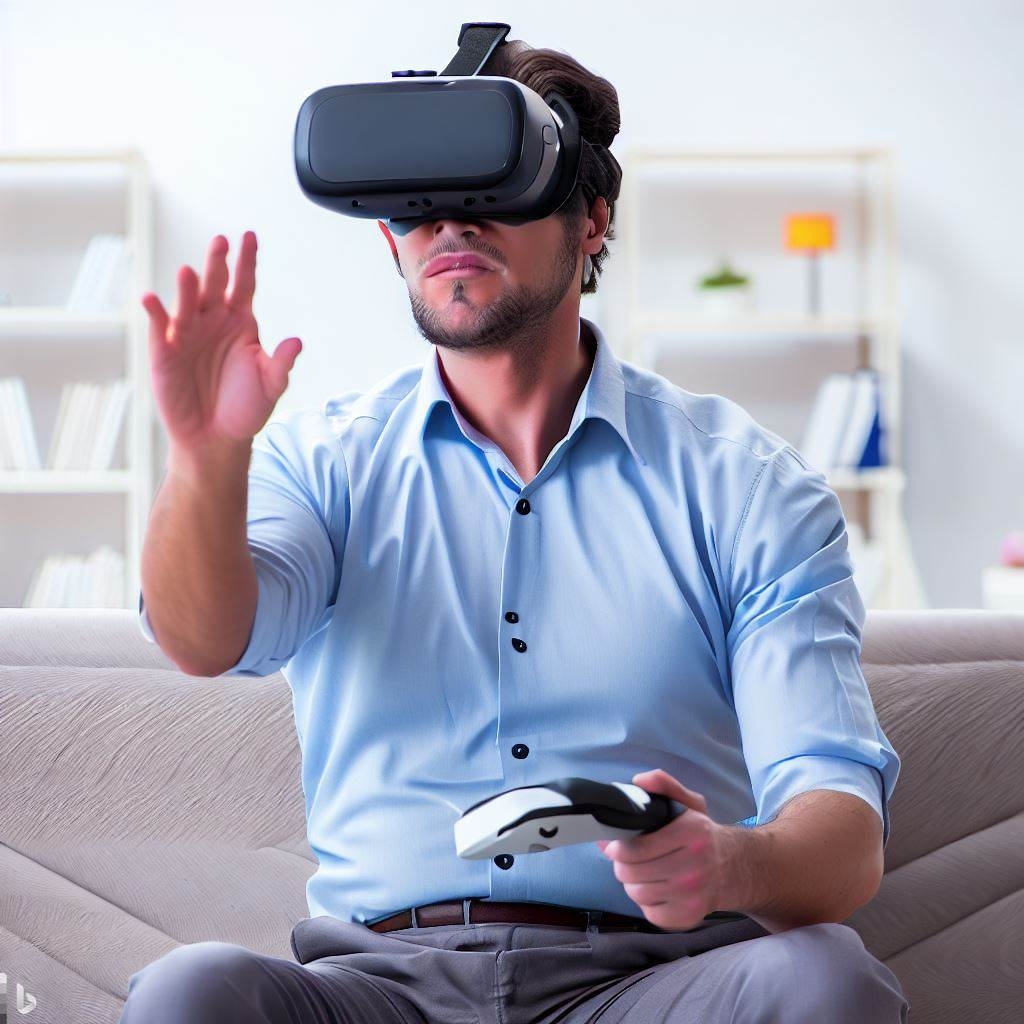
VR-based rehabilitation involves the use of a headset and hand-held controllers to simulate real-life scenarios and movements. The patient is immersed in a virtual environment that challenges them to perform tasks that require the use of their affected limbs. The VR system provides real-time feedback and can be adjusted to the patient’s abilities, making it a personalized and engaging experience.
Studies have shown that VR-based rehabilitation can improve motor function, balance, and gait in stroke patients. In a randomized controlled trial, stroke patients who received VR-based rehabilitation showed greater improvements in upper limb function compared to those who received traditional therapy. Another study found that VR-based rehabilitation improved balance and gait in stroke patients, leading to a reduced risk of falls.
One of the advantages of VR-based rehabilitation is that it can be done remotely, allowing patients to continue their therapy at home. This can be especially beneficial for patients who live in rural areas or have limited access to rehabilitation facilities. Additionally, VR-based rehabilitation can be more cost-effective than traditional therapy, as it requires fewer resources and can be done in shorter sessions.
However, VR-based rehabilitation is not without its limitations. Patients with severe cognitive or visual impairments may not be able to use the technology effectively. Additionally, the cost of VR equipment and software can be a barrier to widespread adoption.
Despite these limitations, VR-based rehabilitation shows great promise in improving outcomes for stroke patients. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that VR-based rehabilitation will become more accessible and affordable. In the meantime, healthcare providers should consider incorporating VR-based rehabilitation into their stroke rehabilitation programs to accelerate recovery and restore motor functions in their patients.